🐍 How to Use Tkinter Listbox to Add and Print Selected Items in Python
If you’re learning Tkinter, Python’s standard GUI library, and want to build a fun and interactive app, this guide is for you! In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to:
- Create a simple Tkinter interface
- Dynamically add items to a Listbox
- Select multiple items
- Print only the selected ones to the console
Let’s get started! 🧑💻
📦 What is Tkinter?
Tkinter is the default GUI (Graphical User Interface) toolkit for Python. It allows you to create windows, buttons, text boxes, and other widgets with minimal code. It’s great for building desktop apps and learning event-driven programming.
🎯 Project Goal
We’ll create a small GUI app that:
- Displays a list of fruits in a Listbox
- Lets the user add more items using an Entry field
- Allows selecting multiple items
- Prints only the selected items to the console
🧑💻 Complete Python Code
Here’s the full working code:
import tkinter as tk
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Fruit Selector")
root.geometry("300x300") # Optional: Set window size
# Function to print selected items
def order():
selected_indices = listBox.curselection()
for i in selected_indices:
print(listBox.get(i))
# Function to add a new item to the Listbox
def add():
listBox.insert(tk.END, addData.get())
addData.delete(0, tk.END) # Clear input after adding
# Create widgets
listBox = tk.Listbox(root,
background="#f7ffde",
selectmode="multiple")
addData = tk.Entry(root, width=20)
submitBtn = tk.Button(root, text="Submit", command=add, width=16)
printBtn = tk.Button(root, text="Print", command=order, width=16)
# Pack widgets
listBox.pack(pady=10)
addData.pack(pady=5)
submitBtn.pack(pady=5)
printBtn.pack(pady=5)
# Add default items
listBox.insert(0, "Mango")
listBox.insert(1, "Banana")
listBox.insert(2, "Apple")
listBox.insert(3, "Guava")
listBox.insert(4, "Pineapple")
# Run the GUI loop
root.mainloop()
🔍 Explanation
1. tk.Listbox(...)
Creates a list where users can select multiple items thanks to selectmode="multiple".
2. curselection()
Returns the index(es) of selected items.
3. get(index)
Fetches the actual value at the specified index.
4. Entry(...)
Lets users type new items to be added to the list.
5. insert(...)
Appends new data to the Listbox.
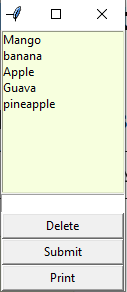
🚀 Output
When you run this code, you’ll see:
- A list of fruits
- An input box to type new items
- A Submit button to add them
- A Print button that prints only the selected items in the terminal
✅ Easy and fun for beginners learning GUI development in Python!
💡 Use Cases
- Grocery item selectors
- Quiz question selectors
- Task list apps
- Any app needing dynamic selection
📈 SEO & Learning Benefits
This simple Tkinter Listbox app helps you understand:
- Event handling
- Widget layout
- User input management
- Dynamic interface updates
Target Keywords:
- Tkinter Listbox add items
- Tkinter print selected items
- Python GUI projects for beginners
- Python Listbox tutorial
🔚 Conclusion
The Tkinter Listbox is a powerful widget that makes user selection in GUIs a breeze. With just a few lines of Python code, you can build dynamic apps with real-time interaction. This project is great for students, hobbyists, and anyone looking to strengthen their Python GUI skills.
✨ Like this tutorial?
✅ Share it
✅ Bookmark it
✅ Comment below with your own Listbox variations!
Let me know if you want a downloadable .zip of the code or if you’d like this styled in a WordPress block format (with HTML/shortcodes) for direct copy-paste!